Tolitoli bay
Totoli is an endangered language of northern Central Sulawesi still spoken by at most 5000 speakers. It is commonly considered a member of the Tomini-Tolitoli group, although it is still unclear whether these languages actually form a genetic group or whether they are just geographically related.
Totoli differs considerably from the other languages of that group with respect to phonology, lexicon and grammar. Conspicuous phonological differences include the frequent occurrence of geminates and the tolerance for closed syllables. Grammatically, Totoli appears to have a unique voice and applicative system which com¬bines features of a typical Philippine-type voice system with features of the applicative systems found in western Indonesia and the southern half of Sulawesi. Although the system is far from being fully understood, it has been suggested that Totoli plays a key role in understanding the change of Philippine-type systems to the kind of symmetrical voice systems found in most west¬ern Indonesian languages (Wolff 1996).
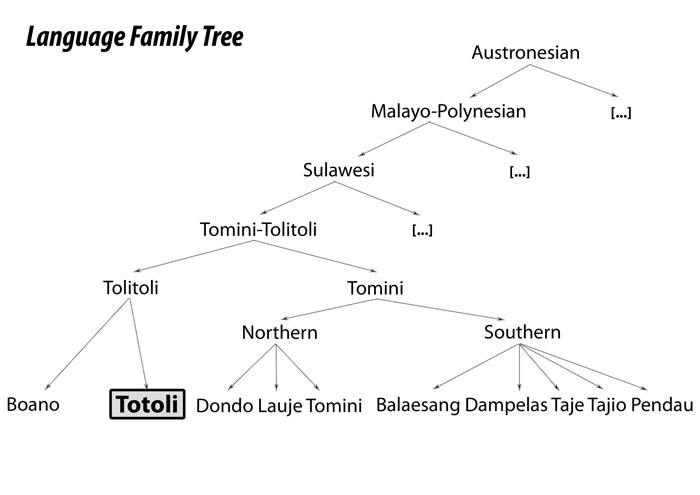
Fig.1: Commonly assumed genetic affiliation of Totoli according to ethnologue.com
References
Adriani, Nicolaus and Albertus C. Kruyt, 1914, De Bare’e-sprekende Toradja’s van Midden Celebes. Vol. III. Batavia: Landsdrukkerij
Barr, Donald F., Sharon G. Barr (in cooperation with C. Salombe), 1979, Languages of Central Sulawesi: Checklists, Preliminary Classification, Language Maps, Word Lists. Ujung Pandang: Hasanuddin University.
Blust, Robert, 1991, The Greater Central Philippines Hypothesis. In Oceanic Linguistics 30/1: 73-129.
Himmelmann, Nikolaus P., 1991, Tomini-Tolitoli Sound Structures. In James N. Sneddon, ed., Studies in Sulawesi Languages, Part II.
Himmelmann, Nikolaus P., 1996, Person Marking and Grammatical Relations in Sulawesi. In Hein Steinhauer, ed., Papers in Austronesian linguistics No. 3, 115-136. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics.
Himmelmann, Nikolaus P., 2001, Sourcebook on Tomini-Tolitoli Languages. General Information and Word Lists. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics.
Inghuong, A. Sofyan, Arfah Adnan, Zohra Mahmud and Masyhuddin Masyhuda, 1983, Struktur Bahasa Totoli. Jakarta: Pusat Pembinaan dan Pengembangan Bahasa.
Inghuong, A. Sofyan, Arfah Adnan, Abdul Gani Hali, Idrus Halim and Nooral Baso, 1985/86b, Morfologi dan Sintaksis Bahasa Totoli. Palu: Proyek Penelitian Bahasa dan Sastra Indonesia dan Daerah Sulawesi Tengah.
Inghuong, A. Sofyan, Ahmad Sarro, Hasan Basri and Dahlan Kajia, 1986/87, Fonologi, morfologi, sintaksis bahasa Bolano. Jakarta: Pusat Pembinaan dan Pengembangan Bahasa.
Kaseng, Syahruddin, Masyhuddin Masyhuda, Abdul Muthalib, Indra B. Wumbu, Amir W. Lumentut, Amir Kadir, Abdul Latif Rozali, 1979, Bahasa-bahasa di Sulawesi Tengah. Jakarta: Pusat Pembinaan dan Pengembangan Bahasa.
Lembaga Bahasa Nasional, 1972, Peta Bahasa-bahasa di Indonesia, Jakarta (= BdK Seri khusus no. 10/1972).
Li, Tania (in cooperation with Sulaiman Mamar), 1991, Culture, Ecology and Livelihood in the Tinombo Region of Central Sulawesi. Jakarta and Halifax: Enviromental Management Development in Indonesia Project.
Masyhuda, Masyhuddin, 1975/81, Bahasa-bahasa Tomini-Tolitoli. Palu: Yayasan Kebudayaan.
Masyhuda, Masyhuddin, 1977, Monografi Daerah Sulawesi Tengah. Jakarta: Proyek Pengembangan Media Kebudayaan.
Noorduyn, J., 1991, A Critical Survey of Studies on the Languages of Sulawesi. Leiden: KITLV Press (=KITLV Bibliographical Series 18).
Stockhoff, W. A. L., ed., 1983, Hollo Lists: Vocabularies in Languages of Indonesia Vol. 7/1: North Sulawesi. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics.
Wumbu, Indra B., Amir Kadir, Nooral Baso and Sy. Maranua, 1986, Inventarisasi Bahasa Daerah di Propinsi Sulawesi Tengah. Jakarta: Pusat Pembinaan dan Pengembangan Bahasa.
Wolff, John U. 1996, The Development of the Passive Verb with Pronominal Prefix in Western Austronesian languages. In Bernd Nothofer, ed., Reconstruction, Classification, Description — Festschrift in Honor of Isidore Dyen. Hamburg: Abera-Verlag.